Prostate Kya Hota Hai
- The prostate gland is a walnut-sized organ essential to the male reproductive system, producing fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
- Common prostate conditions include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer, each with specific symptoms and treatments.
- Prostate size and function change with age, increasing the risk of urinary and reproductive health issues in older men.
- Early detection through blood tests, digital rectal exams, and imaging is vital for managing prostate diseases.
- Healthy lifestyle choices, including diet and regular screening, play a key role in maintaining prostate health and preventing complications.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Understanding the prostate gland is crucial for every man, especially as he ages. This small yet vital part of the male reproductive system plays a major role in producing seminal fluid and supporting sperm health. As men grow older, prostate diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, and prostate cancer become increasingly common. Recognizing how the prostate functions, its significance, and the potential risks can help you take proactive steps in preventing serious health issues and maintaining overall wellness.
Prostate Gland Overview
Many men may not realize the importance of the prostate gland until symptoms of prostate disease appear. The gland sits at the base of the bladder and surrounds the urethra, performing functions that are fundamental for reproduction and urination.
Its primary role within the male reproductive system is to produce fluid that forms part of semen, nourishing and protecting sperm. Conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, and prostate cancer can disrupt these vital functions, leading to significant health challenges if not addressed promptly.
Definition and Function of the Prostate
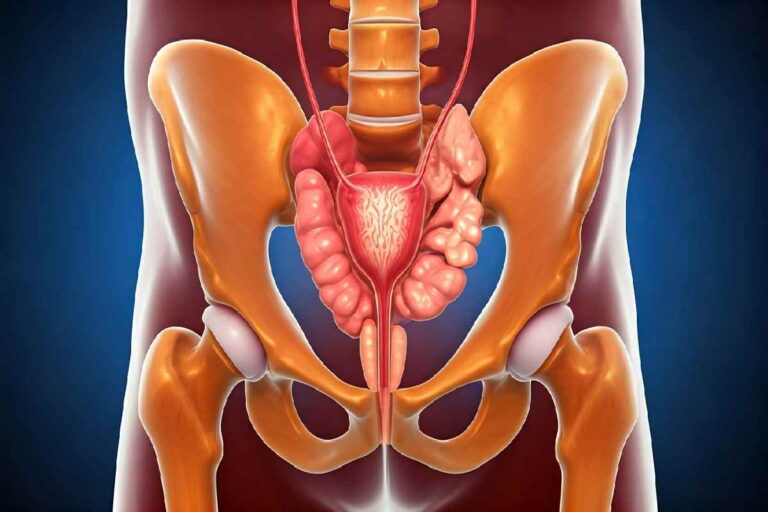
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ found in men, and is a key component of the male reproductive system. It is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, surrounding part of the urethra—the tube through which urine and semen pass out of the body.
One of its main functions is to produce prostatic fluid, which mixes with sperm from the testes and fluids from other glands to create semen. This fluid is slightly alkaline, which helps to neutralize the acidic environment of the vaginal tract, thus protecting sperm and enhancing their ability to fertilize an egg.
Beyond semen production, the prostate also contains enzymes and the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent hormone. This process influences prostate growth and plays a crucial role in male sexual development. Maintaining the health of this gland is essential for both fertility and urinary control.
Role of Prostate in Male Reproductive Health
The prostate is central to male reproductive health. By creating a nourishing fluid, it supports sperm viability, which is essential for successful reproduction. The prostatic fluid, along with sperm, is released through the urethra during ejaculation, ensuring that sperm are protected as they travel through the female reproductive system.
Located at the base of the bladder, the prostate encircles the upper section of the urethra. This positioning means any change in size or structure can directly impact the flow of urine and semen. That’s why urinary symptoms are often the first signs of prostate disease.
The gland’s smooth muscle fibers also help propel semen during ejaculation. If the prostate is not functioning properly, you may experience difficulties with both urination and sexual health. This dual role makes the prostate vital for overall male well-being.
Anatomy and Location of the Prostate
Anatomically, the prostate is a complex gland with several distinct zones, each serving different functions. It lies directly beneath the bladder at the neck and surrounds the prostatic section of the urethra, making its health essential for both urinary and reproductive systems.
The rich blood supply and network of nerves within the prostate support its roles in semen production and ejaculation. Understanding the gland’s unique structure and position is key to recognizing why even small changes in its size or shape can cause significant symptoms, setting the stage for a closer look at its location.
Where is the Prostate Situated in the Body?
The prostate sits inside the pelvis, nestled below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the upper part of the urethra, which is the tube responsible for carrying both urine from the bladder and semen from the reproductive tract out of the body.
This strategic location means the prostate’s health is closely linked to urinary function. When you go for a digital rectal exam, a doctor accesses the prostate through the rectum, as it lies just in front, allowing for easy assessment of size and texture.
Any enlargement or abnormality in the prostate can compress the urethra, leading to symptoms such as difficulty in starting urination, weak urine flow, or frequent urination, especially at night. This makes its position crucial for both the passage of urine and reproductive health.
How Prostate Size and Structure Change With Age
The size of the prostate gland changes throughout a man’s life. At birth, it is small, but it grows rapidly during puberty due to the influence of male hormones. By adulthood, the average prostate weighs about 20 grams, roughly the size of a walnut.
As men reach their thirties, a second growth phase begins. This growth is gradual but can lead to significant enlargement with advancing age, especially after 50. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common age-related condition where the gland becomes larger but remains non-cancerous.
While a slightly enlarged prostate is often normal with age, excessive growth can compress the urethra, causing urinary symptoms. Regular check-ups can help monitor these changes, ensuring any problems are detected and managed early.
Common Prostate Conditions
Prostate health concerns increase with age, and several conditions can affect this important gland. The most common issues include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer, each presenting with unique challenges and symptoms.
BPH leads to an enlarged prostate, often resulting in urinary difficulties, while prostatitis is inflammation that may cause pain or discomfort. Prostate cancer, although sometimes symptomless in early stages, can become serious if not detected and treated promptly. Let’s explore these conditions in detail.
Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)
An enlarged prostate, known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is common as men age, significantly impacting the lower urinary tract. This condition occurs when the prostate gland grows, affecting the flow of urine due to pressure at the neck of the bladder. BPH can lead to symptoms like frequent urination, difficulty starting and stopping urination, and incontinence. Diagnosis typically involves a digital rectal examination and a PSA blood test, with treatment options ranging from medication to surgical interventions like transurethral resection of the prostate.
Prostate Inflammation (Prostatitis)
Inflammation of the prostate, or prostatitis, can significantly affect the male reproductive system and overall health. This condition often leads to lower urinary tract symptoms, such as painful urination or difficulty emptying the bladder. Chronic prostatitis may be caused by bacterial infections or non-bacterial factors, leading to persistent discomfort and inflammation. Treatments typically involve antibiotics for bacterial prostatitis, pain management, and sometimes surgical interventions, depending on severity. Regular digital rectal examinations can aid in early detection and provide crucial insights into prostate health.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the leading cancers affecting men, particularly as they age. In most cases, cancer cells develop slowly within the prostate gland, but some types can be aggressive and spread to other organs, a process known as metastatic prostate cancer.
Early detection is crucial, as symptoms may not appear until the disease has progressed. Treatment options such as radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy can be highly effective, especially when diagnosis occurs at an early stage.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer usually develops slowly, often causing no symptoms in its earliest stages. As the disease progresses, you might experience signs similar to other prostate conditions, including difficulties with urination, a weak stream, or an urgent need to use the bathroom.
You may also notice blood in your urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, and, in some cases, erectile dysfunction. These symptoms are not exclusive to cancer and can result from benign conditions like BPH or prostatitis, making it important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis.
A quote from Dr. Anthony D’Amico, Harvard Medical School, highlights the need for vigilance: “Early-stage prostate cancer is often silent. Men should talk to their doctors about screening, especially if they have risk factors.” Timely assessment and regular screening increase the chances of detecting prostate cancer before it spreads.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Prostate Cancer
Certain factors increase your risk for developing prostate cancer. Advancing age is the greatest risk, with most cases occurring in men over 50. Family history also plays a crucial role, as does being of African American descent. Other contributors include obesity and certain dietary habits.
- Men over 50 are at higher risk.
- A family history of prostate cancer increases susceptibility.
- African American men have a greater likelihood of developing the disease.
- Obesity and a diet high in red meat may add to the risk.
Prevention focuses on regular screening and making positive lifestyle choices. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, staying active, and having regular check-ups all help reduce your risk. Early conversations with your doctor are important, especially if you have a family history of prostate issues.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Caring for your prostate goes beyond just medical checks; it’s about daily choices. Simple lifestyle changes—including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management—can significantly reduce your risk for prostate disease and associated health problems.
Prevention also means staying informed about regular screening and knowing the early signs of trouble. Healthy habits not only protect your prostate but contribute to your overall well-being. Let’s look deeper into the specific lifestyle and dietary adjustments that support prostate health.
Lifestyle Habits for a Healthy Prostate
Your daily routine plays a big part in maintaining prostate health. Regular exercise is essential—not only does it control weight, but it also helps lower blood pressure and improve overall circulation, both of which are linked to reduced prostate risks.
Simple lifestyle choices to adopt include:
- Staying physically active with activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Managing high blood pressure with regular check-ups.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through portion control and mindful eating.
If you have health insurance, use it for annual exams and early screenings. These habits not only lower the risk of prostate disease but also enhance your quality of life as you age.
Dietary Choices and Regular Screening Tips
What you eat significantly impacts your prostate health. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting red meat and processed foods. Foods high in antioxidants, such as tomatoes, berries, and leafy greens, are especially beneficial.
Regular screening is equally important. PSA blood tests and digital rectal exams can catch problems early, even before symptoms arise. If your doctor recommends it, an ultrasound may be used to check for abnormalities in prostate size and structure.
Don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Proactive dietary choices and annual health checks can help you stay ahead of potential issues, giving you the best chance for a healthy, active life.
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने के लक्षण क्या है?
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने के प्रमुख लक्षणों में पेशाब में रुकावट, कमजोर या धीमा फ्लो, बार-बार पेशाब आना, और रात में बार-बार उठना शामिल हैं। कई बार पूरे मूत्राशय का खाली न होना महसूस हो सकता है, जिससे बार-बार जाने की आवश्यकता महसूस होती है। पेशाब के बाद भी जलन या दर्द होना, मूत्र में रक्त आना, और अचानक पेशाब की तीव्र आवश्यकता भी सामान्य संकेत हैं।
ये लक्षण मुख्य रूप से प्रोस्टेट के बढ़ने से मूत्रमार्ग पर दबाव बनने के कारण होते हैं। समय रहते पहचान और उपचार से आप गंभीर समस्याओं से बच सकते हैं। अगर आपको इन लक्षणों का अनुभव हो, तो डॉक्टर से संपर्क करना जरूरी है।
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने के कारण क्या है?
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने का सबसे सामान्य कारण उम्र बढ़ना है। जैसे-जैसे पुरुषों की उम्र 50 के पार जाती है, हार्मोनल बदलाव और टेस्टोस्टेरोन के स्तर में परिवर्तन प्रोस्टेट के आकार में वृद्धि कर सकते हैं। BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) इसी प्रक्रिया का परिणाम है, जिसमें ग्रंथि कैंसर रहित तरीके से बढ़ती है।
परिवार में प्रोस्टेट संबंधी रोग का इतिहास, मोटापा, शारीरिक निष्क्रियता और जीवनशैली भी इसके जोखिम को बढ़ाते हैं। कुछ मामलों में उच्च रक्तचाप और डाइट में असंतुलन भी जिम्मेदार हो सकते हैं। कारण चाहे जो भी हो, समय पर जांच और सही जानकारी से उपचार संभव है।
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने के लिए कौन से टेस्ट होते हैं?
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने की जांच के लिए कुछ प्रमुख टेस्ट किए जाते हैं। इनमें ब्लड टेस्ट (PSA), डिजिटल रेक्टल एग्जाम (DRE), और अल्ट्रासाउंड प्रमुख हैं। PSA टेस्ट से खून में प्रोस्टेट स्पेसिफिक एंटीजन की मात्रा मापी जाती है, जिससे प्रोस्टेट के रोग या कैंसर का अनुमान लगाया जा सकता है।
- ब्लड टेस्ट (PSA): प्रोस्टेट की स्वास्थ्य स्थिति जानने के लिए।
- डिजिटल रेक्टल एग्जाम: प्रोस्टेट का आकार और सख्ती जांचने हेतु।
- अल्ट्रासाउंड: प्रोस्टेट की इमेजिंग और सटीक आकार जानने के लिए।
इन टेस्ट्स के जरिए प्रोस्टेट की समस्या की पहचान और उचित इलाज की दिशा तय होती है।
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने का उपचार क्या है?
प्रोस्टेट बढ़ने का उपचार रोगी की उम्र, लक्षणों की गंभीरता, और प्रोस्टेट के आकार पर निर्भर करता है। हल्के मामलों में जीवनशैली में बदलाव और दवाओं से राहत मिल सकती है, जबकि गंभीर मामलों में सर्जरी की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। सबसे सामान्य सर्जिकल प्रक्रिया ट्रान्सयूरेथ्रल रिसेक्शन ऑफ द प्रोस्टेट (TURP) है।
- दवाएं: पेशाब की परेशानी कम करने और ग्रंथि को छोटा करने के लिए।
- प्रोस्टेट सर्जरी (TURP): गंभीर मामलों में मूत्रमार्ग की रुकावट दूर करने हेतु।
- लाइफस्टाइल बदलाव: डाइट में सुधार, व्यायाम, और नियमित जांच।
सही समय पर उपचार से जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार संभव है।
Causes
Aging is the most significant cause of prostate disease, especially benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As men age, hormonal changes—particularly fluctuations in testosterone and DHT—cause the prostate to grow. Other contributing causes include a family history of prostate problems, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Factors like high blood pressure, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can also raise the risk. Recognizing these causes makes it possible to take preventive actions early. Addressing these risk factors can help you avoid or delay the onset of troublesome prostate symptoms.
Symptoms
Symptoms of prostate issues often center on changes in urination. You might notice trouble starting or stopping urine flow, a weak or interrupted stream, or the feeling that your bladder is never fully empty. Frequent urination, especially at night, and a sudden, urgent need to go are typical signs.
Some men experience pain during urination, blood in the urine, or even discomfort in the lower back or pelvic area. These lower urinary tract symptoms should never be ignored, as they may indicate not only benign conditions but also more serious issues such as prostate cancer.
Exams and Tests
Diagnosing prostate enlargement or disease involves a combination of exams and laboratory tests. These help your doctor assess prostate size, structure, and function, and detect any abnormalities early.
Below is a summary of the most commonly used tests:
| Test Name | Purpose/Description |
|---|---|
| PSA (Blood Test) | Measures prostate-specific antigen levels; high levels may indicate prostate disease or cancer. |
| Digital Rectal Examination | Doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to feel for changes in prostate size, shape, or texture. |
| Ultrasound | Imaging technique (usually transrectal) that visualizes prostate size and detects abnormalities. |
| Urinalysis | Checks for infection or blood in urine, which may accompany prostate conditions. |
Regular screening makes it possible to catch problems before they become serious, supporting better long-term outcomes.
Treatment
Treatment for prostate enlargement or disease depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. For BPH, medications that relax muscles or shrink the gland are commonly prescribed. In more advanced cases, surgical options such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or prostatectomy may be needed.
For prostate cancer, treatment can include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or a combination. Your doctor will consider your age, health, and personal preferences when recommending options. Early intervention improves outcomes, so discussing symptoms or risk factors with your healthcare provider is essential.
Support Groups
Living with prostate disease can be challenging, but you don’t have to face it alone. Support groups provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and get emotional support from others who understand what you’re going through.
Many organizations and online communities offer resources tailored specifically for men with prostate conditions:
- Local hospital-based or community support groups.
- Online forums and national organizations for prostate cancer and BPH.
- Health insurance providers often offer access to educational materials and counseling.
Joining a support group can help you manage stress, learn practical tips for daily challenges, and feel empowered to take charge of your health.
Possible Complications
If prostate conditions are left untreated, complications can develop. For example, severe enlargement or chronic inflammation may lead to urinary incontinence, where you lose control over urination. Chronic prostatitis can cause ongoing pelvic pain and discomfort.
Other potential complications include erectile dysfunction and, in rare cases, kidney problems if urinary retention becomes severe. Managing symptoms and seeking timely treatment greatly reduces your risk of long-term issues. Addressing complications early helps you maintain your quality of life and overall health.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience any symptoms of prostate disease, such as persistent difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pelvic pain. Don’t ignore sudden or severe symptoms—these may indicate an urgent need for evaluation.
Even if your symptoms seem mild, early consultation allows for early detection and better management. Remember, many prostate conditions are treatable, especially when addressed promptly. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are a vital part of staying healthy as you age.
Alternative Names
The prostate gland is sometimes referred to by different names depending on the language or context. Common alternative terms include “prostatic gland” and “male reproductive gland.” When discussing specific conditions, benign prostatic hyperplasia is often called “BPH,” while inflammation of the prostate is termed “prostatitis.”
In medical literature, you might also see references to terms like “enlarged prostate,” “chronic pelvic pain syndrome,” or simply “prostate disease.” Knowing these alternative names can help you understand medical reports or talk to your doctor more effectively about your health concerns.
Patient Instructions
Following your doctor’s instructions is essential if you have been diagnosed with a prostate problem or have undergone prostate surgery. Always take medications as prescribed, attend follow-up appointments, and inform your healthcare provider about any changes in symptoms.
After surgery or during ongoing treatment, stay hydrated, avoid strenuous activities until cleared, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Practicing pelvic floor exercises can also improve urinary control. Staying informed and proactive helps you recover faster and keeps your prostate health on track.
Conclusion – Prostate Kya Hota Hai
Prostate health is a critical aspect of male well-being that should not be overlooked. Understanding the anatomy, function, and common conditions related to the prostate empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. From recognizing the early signs of prostate cancer to adopting lifestyle habits that promote a healthy prostate, knowledge is key. Regular screenings and a proactive approach to diet and exercise can significantly impact prostate health. Remember, taking care of your prostate is taking care of yourself. If you have questions or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to reach out for a free consultation with our experts. Your health is worth it!
Frequently Asked Questions
Prostate Enlargement ke mukhya lakshan kya hain?
Prostate enlargement ke mukhya lakshan hain—peshab karne mein mushkil, halka ya ruk-ruk kar aana, baar-baar peshab ki zarurat, raat mein uth kar peshab करना, aur bladder khali na hone ka ehsaas. In symptoms ko ignore na karein.
Prostate ki health banaye rakhne ke liye kaun se changes zaruri hain?
Prostate ki health ke liye healthy diet lena, regular exercise karna, tobacco aur alcohol se bachna, aur routine screening karwana zaruri hai. High blood pressure control mein rakhna bhi prostate ko healthy banaye rakhne mein madad karta hai.
Prostate cancer ka ilaj aur treatment options kya hain?
Prostate cancer ka treatment stage aur health condition par depend karta hai. Options mein prostatectomy (surgery), radiation therapy, hormone therapy, aur kuch cases mein chemotherapy shaamil hain. Jaldi detection se outcome behtar hota hai.