Peptide Pathways in Energy and Glucose Control
The global rise in obesity and metabolic syndrome has driven intense scientific interest in peptide-based regulators of energy balance, glucose control, and mitochondrial function. Peptides—due to their specificity, biocompatibility, and versatility—represent one of the most promising classes of biomolecules under investigation for modulating metabolism at the cellular and systemic level.
This article reviews the most recent research findings on peptides that influence insulin sensitivity, fat oxidation, appetite regulation, and mitochondrial performance. The information presented is derived from peer-reviewed publications and is intended solely for research and educational purposes. All peptides discussed are not for human use.
Table of Contents
1. GLP-1 and GLP-2 Analogs: Beyond Glucose Control
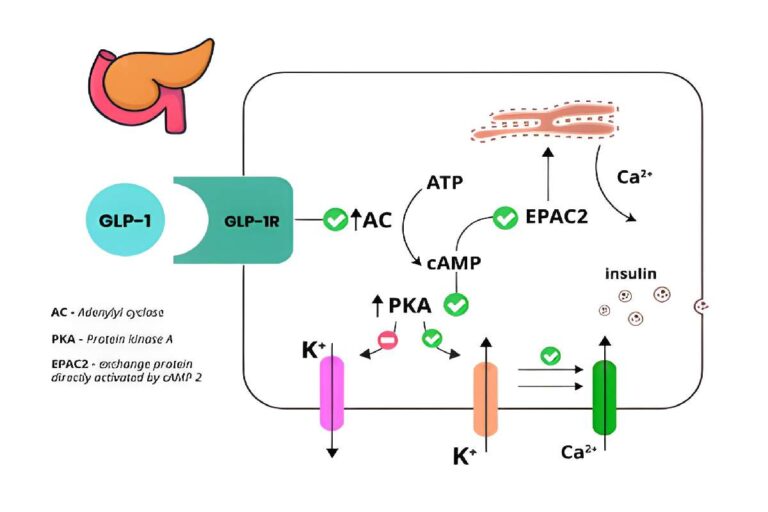
The incretin peptides **GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1)** and **GLP-2** have been the focus of metabolic research for over a decade. GLP-1 enhances insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying, effectively improving postprandial glucose control. Its analogs, designed to resist DPP-IV degradation, demonstrate sustained activity and greater therapeutic durability in preclinical models.
Recent studies have shown that dual or triagonists combining GLP-1 with GIP or glucagon receptor activation yield enhanced weight loss and glycemic outcomes by increasing energy expenditure. Furthermore, GLP-1 analogs influence appetite centers in the hypothalamus, reducing caloric intake and modulating reward pathways linked to food consumption.
GLP-2, though less known for metabolic control, plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity and lipid metabolism. It reduces systemic endotoxemia and inflammation—two critical drivers of insulin resistance . Together, GLP-1 and GLP-2 represent a dual axis of metabolic and gut-mediated regulation, forming the foundation of incretin-based research.
2. MOTS-c: The Exercise-Mimetic Peptide
**MOTS-c**, a mitochondrial-derived peptide, is one of the most compelling new targets for metabolic research. It enhances AMPK activation, increases glucose uptake, and promotes fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle, effectively mimicking the metabolic benefits of exercise.
Preclinical data show that MOTS-c improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice, increases mitochondrial biogenesis, and enhances endurance performance. In aged models, it restores youthful metabolic flexibility by upregulating PGC-1α and SIRT1—genes central to mitochondrial renewal.
Circulating MOTS-c levels decline with age, suggesting a link between mitochondrial peptide signaling and the onset of metabolic decline. The growing interest in MOTS-c as a “metabolic stabilizer” has led to active exploration of its role in hepatic glucose control, obesity prevention, and muscle mitochondrial communication.
3. Adipokinetic and Lipolytic Peptides
Research on energy mobilization has also turned to peptides that directly regulate lipid metabolism and fat oxidation. The **melanocortin system**, particularly through α-MSH and MC4R activation, plays a pivotal role in reducing food intake and increasing thermogenesis. MC4R agonist peptides have demonstrated robust reductions in adiposity in animal studies by elevating sympathetic outflow and mitochondrial uncoupling.
Similarly, **ghrelin antagonistic peptides** are under investigation for their ability to suppress hunger signals. Early-stage findings show that ghrelin receptor blockers reduce meal frequency and body weight without adverse metabolic effects.
Peptides affecting **adiponectin** and **leptin** pathways also offer new insights. Adiponectin-derived peptides enhance fatty acid oxidation, while leptin-mimetic peptides restore signaling sensitivity in leptin-resistant models. These findings illustrate the broad peptide influence on adipose regulation and energy utilization.
4. Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress Regulation
Metabolic homeostasis depends on efficient mitochondrial energy conversion. Mitochondria-targeted peptides such as **SS-31 (elamipretide)** improve oxidative phosphorylation and protect against lipid peroxidation. In animal models of diet-induced obesity, SS-31 restored cardiac and skeletal muscle ATP levels and enhanced glucose oxidation.
**Humanin**, another mitochondrial peptide, reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress and protects β-cells from oxidative injury. Combined with MOTS-c, it forms part of a mitochondrial regulatory network that integrates stress adaptation with metabolic flexibility.
These peptides’ ability to reduce ROS accumulation and sustain ATP production under metabolic overload makes them valuable for understanding insulin resistance and mitochondrial aging at the cellular level.
5. Gut-Brain Axis and Metabolic Inflammation
Emerging research emphasizes the **gut-brain axis** as a central hub in metabolic regulation. Peptides influencing both gut permeability and central appetite pathways hold dual potential for obesity and diabetes research.
GLP-2 and KPV (Lys-Pro-Val) improve gut barrier integrity, reducing circulating endotoxins and systemic inflammation. A healthier barrier limits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release, preventing metabolic endotoxemia—a major contributor to insulin resistance.
At the neural level, peptides like melanocortin analogs, oxytocin fragments, and amylin derivatives act on hypothalamic nuclei to suppress appetite while promoting energy expenditure. These centrally acting peptides demonstrate that controlling energy homeostasis requires synchronized communication between gut peptides and neuropeptide systems.
6. Integration and Future Research Directions
Peptide Pathways in Energy and Glucose Control. Metabolic health peptide research now spans multiple biological axes—gut, brain, muscle, and mitochondria—offering a multi-system perspective on weight and glucose regulation. The integration of mitochondrial-derived peptides (like MOTS-c and humanin) with incretin analogs (GLP-1/GLP-2) and melanocortin modulators points toward comprehensive energy reprogramming strategies.
Future research is focusing on optimizing peptide half-life, enhancing oral or transdermal delivery, and combining multi-pathway peptides in single formulations. Early exploration of **MOTS-c and SS-31 co-administration** shows synergistic mitochondrial reinforcement and enhanced glucose tolerance.
While no peptide therapy is yet approved for metabolic longevity enhancement, the collective findings point to an evolving framework—where peptides act not merely as hormones but as dynamic regulators of energy homeostasis and cellular rejuvenation.
To find and discover more exciting research peptides for sale, visit PureTestedPeptides.com for verified research-grade materials.
Peptide Pathways in Energy and Glucose Control. For more research findings and access to high-purity peptides designed for laboratory investigation, visit PureTestedPeptides.com — a trusted source for peptides for research purposes only.